 Health
Health
Counterfeit Rabies Vaccine Alert: Australia Warns of Fake Abhayrab Doses Circulating in India Since 2023
Australia's Technical Advisory Group on Immunisation has issued an urgent public health alert warning that people who received the rabies vaccine Abhayrab in India from November 1, 2023 onwards may have received counterfeit, ineffective doses. The alert, released December 22, 2025, follows investigations revealing that fake versions of Abhayrab entered the Indian market, potentially leaving millions of recipients unprotected against rabies—a disease that is almost always fatal once symptoms develop. Indian Immunologicals Limited, the vaccine manufacturer, identified the counterfeit products in early 2025, noting that counterfeiters had replicated genuine batch numbers, packaging, and labeling with precision, making authentic and fake vials indistinguishable. The counterfeit vaccines may lack the active antigen necessary for immunity or may have been stored outside required temperature-controlled supply chains, rendering them completely ineffective. Counterfeit doses have been identified in major Indian cities including Delhi, Mumbai, Ahmedabad, and Lucknow, though the complete distribution extent remains unclear. Australian health authorities are recommending that anyone vaccinated with Abhayrab or any rabies vaccine during the affected period in India immediately consult healthcare providers and receive replacement doses using registered vaccines. This alert highlights critical vulnerabilities in pharmaceutical supply chains and underscores the serious public health risks posed by counterfeit life-saving vaccines in regions where rabies remains endemic.
 Health
Health
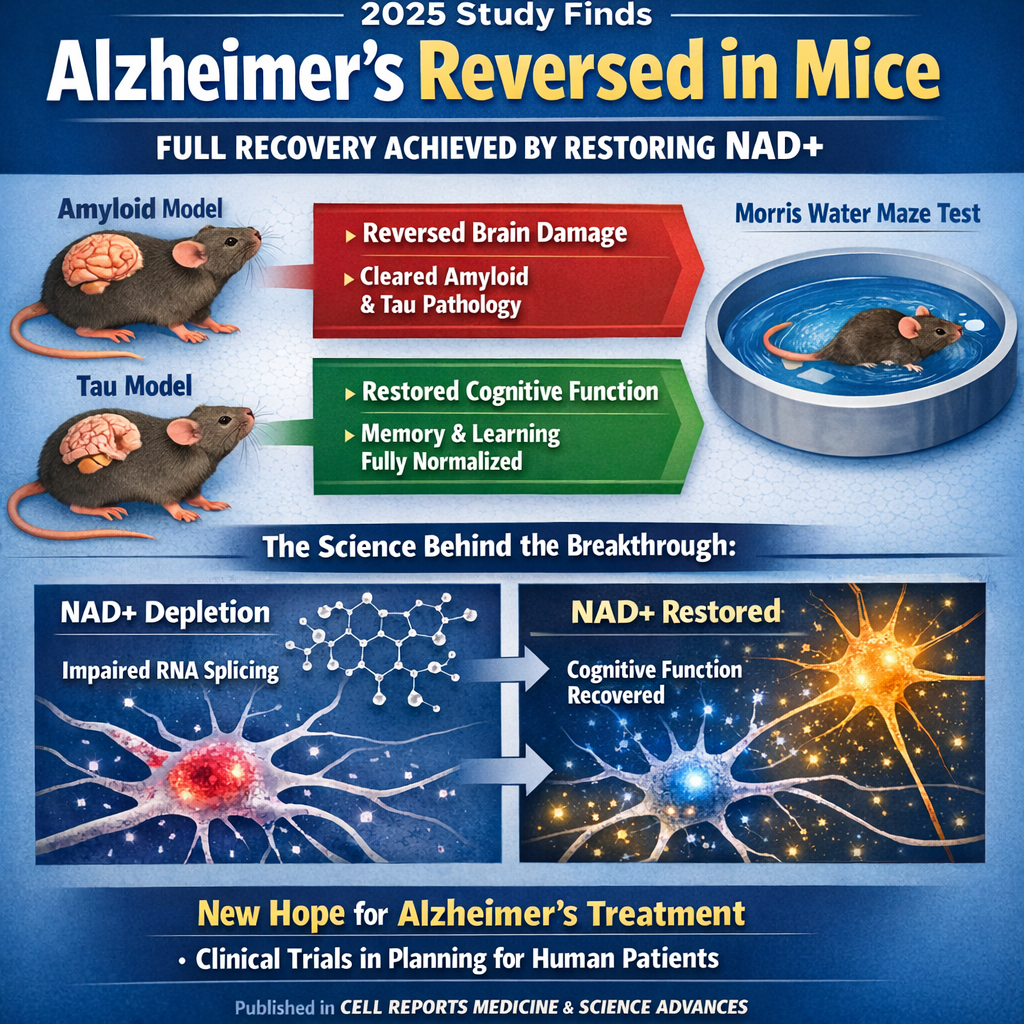
Alzheimer's Disease Reversed in Mice Through NAD+ Restoration: Groundbreaking Research Offers Hope for Human Treatment
A landmark 2025 study led by researchers at Case Western Reserve University and University Hospitals has demonstrated that Alzheimer's disease can be reversed in mice—a finding that directly challenges the long-held scientific assumption that Alzheimer's is irreversible once cognitive decline begins. Using two distinct Alzheimer's mouse models (one with amyloid pathology, one with tau pathology), researchers showed that restoring NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide)—a crucial molecule for cellular energy—fully reversed advanced Alzheimer's-related brain damage and completely restored cognitive and memory function. The treatment, using the pharmacological compound P7C3-A20, achieved pathological and functional recovery in both disease models, with treated mice performing identically to healthy controls on standardized memory tests including the Morris water maze. The breakthrough reveals that Alzheimer's pathology, long viewed as irreversible neuronal death, may actually reflect reversible dysfunction in brain energy metabolism. Research published in Cell Reports Medicine and follow-up studies in Science Advances uncovered the underlying mechanism: NAD+ depletion impairs alternative RNA splicing, causing neuronal dysfunction and cognitive decline—a process that can be reversed by restoring NAD+ balance. These discoveries open unprecedented therapeutic possibilities and have initiated clinical trial planning for human Alzheimer's treatment, potentially transforming Alzheimer's from an irreversible death sentence into a treatable condition.
 Health
Health
Low Alcohol Consumption Increases Oral Cancer Risk in Indian Men: New Research Challenges Safe Drinking Myths
A landmark study examining alcohol consumption patterns in the Indian population reveals that even low levels of alcohol intake substantially increase oral cancer risk in men—challenging widely-held beliefs that "moderate" or "safe" drinking thresholds exist. Research demonstrates that oral cavity cancer, one of India's most prevalent cancers (accounting for 28% of male cancers and 7% of female cancers), shows strong dose-response relationships with alcohol consumption, meaning that any level of drinking increases risk, with higher consumption producing proportionally greater increases. The study found that alcohol consumption increases oral cancer risk by approximately two-fold, with risk escalating further when alcohol combines with other risk factors including tobacco smoking and betel quid chewing. Critically, the research challenges the notion of a "safe" threshold of alcohol consumption—even low levels of regular drinking carry measurable cancer risk. The implications are particularly significant for Indian populations given the high prevalence of alcohol consumption, betel quid chewing, and tobacco use, creating multiplicative risk profiles. Understanding alcohol's independent carcinogenic effects, population-specific risk factors, and the absence of truly "safe" consumption levels enables individuals and public health authorities to make informed decisions regarding cancer prevention and health protection.
 Health
Health
Three Essential Habits to Strengthen Your Mental Resilience in 2026: Expert Strategies for Lasting Psychological Well-Being
Mental strength and emotional resilience have become critical life skills in our increasingly complex, stress-filled modern world. As 2026 begins, experts in psychology and mental health emphasize that building genuine mental strength requires specific, evidence-based habits practiced consistently rather than occasional wellness activities. Research demonstrates that resilience is trainable through deliberate practice, with three foundational habits emerging as most powerful for building mental toughness: mindful awareness and self-compassion (enabling emotional regulation and acceptance), gratitude practice and positive reflection (rewiring neural pathways toward resourcefulness and meaning), and purposeful physical movement combined with restorative rest (regulating stress hormones and supporting neurological health). These three habit categories, grounded in cognitive behavioral therapy, neuroscience research, and decades of psychological practice, work synergistically to build emotional reserves enabling individuals to navigate adversity, manage stress, recover from setbacks, and thrive amid life's inevitable challenges. Unlike aspirational wellness goals often abandoned by February, these specific, implementable habits designed for consistency and sustainability offer genuine potential to strengthen mental resilience throughout 2026 and beyond.
 Health
Health
Pig Organ Xenotransplantation: How Genetically Engineered Animal Organs Could Revolutionize Transplant Medicine
Xenotransplantation—transplanting genetically engineered organs from pigs to humans—represents a revolutionary breakthrough in transplant medicine with the potential to fundamentally solve the global organ shortage crisis. Over 90,000 patients currently await kidney transplants in the United States alone, with only one-third ever receiving a transplant, while thousands die annually while waiting. Recent groundbreaking achievements in 2025 include FDA approval for the first clinical trials of genetically modified pig kidneys in living human patients, landmark surgical procedures transplanting pig kidneys that functioned for over three months, and innovative advances in genetic engineering producing pigs with 10 targeted genetic modifications. Experts now suggest that pig organs could eventually become superior to human donor organs through precise genetic engineering, controlled quality, elimination of infections, optimized organ sizing, and elective transplant timing before patients deteriorate. Gene-edited pig organs have demonstrated remarkable long-term survival in nonhuman primates (exceeding one year in some cases) and are now transitioning from experimental laboratory studies to clinical application. Understanding xenotransplantation's scientific advances, remaining challenges including immune rejection and infection risk, ethical considerations, and clinical outlook reveals how this transformative technology may reshape transplant medicine and provide hope to millions suffering from end-stage organ disease.
 Health
Health
How ADHD Medications Actually Work: The Surprising Science Behind Stimulant Attention Improvement
Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) affects approximately 5-7% of children and nearly 2-3% of adults worldwide, characterized by persistent difficulties with attention, impulse control, and executive function. Contrary to popular misconception, ADHD stimulant medications like methylphenidate (Ritalin) and amphetamines (Adderall) do not directly enhance attention through overstimulation. Instead, they work through sophisticated neuropharmacological mechanisms involving dopamine and norepinephrine neurotransmitter systems. Recent 2025 research using advanced neuroimaging and network analysis demonstrates that stimulant medications stabilize dynamic brain network organization—reducing excessive neural flexibility and creating more organized, task-focused brain activity patterns. These medications increase synaptic concentrations of dopamine and norepinephrine by blocking their reuptake, which enhances prefrontal cortex function (the brain region controlling attention, working memory, impulse control, and executive functions). Through modulation of dopamine D1 and D2 receptors, stimulants enhance task-relevant neural representations while suppressing task-irrelevant distractions, effectively improving attention through indirect mechanisms. Understanding how ADHD medications actually work provides insight into why they benefit 80% of children with ADHD, how to optimize treatment, and potential development of even more targeted therapeutic approaches.
 Health
Health
Blood Test for Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Risk: Revolutionary Biomarker Discovery Enables Early Detection of Inherited Heart Disease
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM), the most common inherited heart disease affecting approximately 1 in 500 people worldwide, can be silently progressive and may lead to sudden cardiac death with no prior warning signs. Recent groundbreaking research in 2025 demonstrates that novel blood-based biomarkers can accurately predict risk of developing hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and identify individuals at high risk for major adverse cardiovascular events, including sudden cardiac death. These circulating biomarkers—measurable proteins and metabolites in the blood—offer unprecedented diagnostic and prognostic potential that surpasses conventional clinical risk assessment tools. Machine learning algorithms analyzing proteomics panels (comprehensive protein profiles) from blood samples achieved diagnostic accuracy exceeding 80% for identifying HCM, with sensitivity and specificity approaching 100% in some studies. This transformative advancement enables earlier disease detection in genetically at-risk individuals before symptoms develop, allows targeted risk stratification to identify those requiring intensive monitoring or intervention, facilitates family screening to identify asymptomatic carriers, and may revolutionize HCM management by enabling preventive interventions before irreversible cardiac damage occurs. Understanding blood-based biomarkers, their clinical application, and implications for inherited heart disease diagnosis represents a critical frontier in precision cardiology and preventive medicine.
 Health
Health
Super Agers: The Science of Exceptional Brain Health in Your 80s and 90s—Expert Tips for Cognitive Longevity
"Super agers" are a remarkable group of individuals age 80 and older whose memory and cognitive abilities match or exceed those of people 20-30 years younger. Over 25 years of groundbreaking research from Northwestern University and international collaborators has identified the biological, neurological, and behavioral characteristics that enable super agers to resist typical age-related cognitive decline and maintain exceptional mental sharpness well into their 80s, 90s, and beyond. Brain imaging studies reveal that super agers possess distinctive neurobiological signatures: thicker cortexes resistant to age-related shrinkage, larger and healthier neurons in memory-critical brain regions, higher densities of specialized von Economo neurons linked to social intelligence, and superior white matter preservation. Critically, research demonstrates that cognitive decline is not inevitable, and that specific lifestyle factors—particularly robust social connections, regular physical and cognitive exercise, healthy nutrition, quality sleep, and stress management—significantly contribute to maintaining cognitive reserve and resisting dementia. These findings challenge long-held assumptions about aging and offer actionable strategies for anyone seeking to preserve brain health and independence into advanced age.
 Health
Health
Male Factor Infertility: Why This Often-Overlooked Diagnosis Demands Comprehensive Couple Evaluation
Male factor infertility contributes to approximately 30-50% of couples' inability to conceive, yet remains frequently overlooked or inadequately evaluated in clinical practice. A comprehensive review of infertility evaluation emphasizes that male factor assessment is often neglected in favor of focusing diagnostic efforts exclusively on female partners, leading to delays in identifying correctable male conditions and unnecessary procedures in female partners. Contemporary evidence demonstrates that complete couple infertility evaluation—including thorough male assessment through medical history, physical examination, semen analysis, hormonal evaluation, and advanced testing—significantly improves diagnostic accuracy and enables targeted treatment strategies. Male infertility encompasses diverse etiologies ranging from correctable hormonal abnormalities and obstructive conditions amenable to surgery, to genetic abnormalities and primary testicular dysfunction. Understanding the breadth of male-factor evaluation, recognizing common causes of male infertility, and implementing evidence-based diagnostic protocols enables healthcare providers to identify and treat conditions previously left undiagnosed, improving fertility outcomes for couples and preventing unnecessary procedures in female partners with normal fertility.
 Health
Health
2026 New Year's Resolutions: Expert-Backed Strategies to Achieve Your Health and Fitness Goals
As 2026 begins, millions of people worldwide commit to New Year's resolutions focused on health, fitness, and lifestyle improvements. However, research reveals that approximately 80% of New Year's resolutions fail by mid-February without proper planning and support. Behavioral science research demonstrates that people who formalize their goals are 10 times more likely to achieve them compared to those attempting change without explicit resolutions. Success requires moving beyond vague aspirations to create SMART goals (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound), develop comprehensive action plans, build accountability through social support, practice self-compassion when setbacks occur, and maintain consistency over perfection. This comprehensive guide draws on evidence-based strategies from behavioral science, psychology, fitness experts, and healthcare professionals to transform 2026 into a year of sustainable health transformation and lasting lifestyle change.
 Health
Health
High-Fat Cheese and Cream for Brain Health: A 25-Year Study Links Full-Fat Dairy to Lower Dementia Risk
A groundbreaking 25-year Swedish study published in December 2025 in Neurology, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology, reveals a surprising association between consuming high-fat cheese and cream and reduced dementia risk. The research tracked 27,670 participants and found that those consuming 50 grams or more of high-fat cheese daily (containing more than 20% fat)—equivalent to approximately five regular slices—had a 13% lower risk of developing dementia compared to those eating less than 15 grams daily. Even more striking, high-fat cheese consumption was associated with a 29% lower risk of vascular dementia, the second most common form of dementia. Similarly, participants consuming 20 grams or more of high-fat cream daily showed a 16% lower risk of developing dementia. These findings challenge decades of dietary guidance emphasizing low-fat alternatives and suggest that not all dairy products affect brain health equally, with fermented high-fat products offering potential neuroprotective benefits through bioactive compounds, improved vascular health, and omega-3 fatty acid content.
 Health
Health
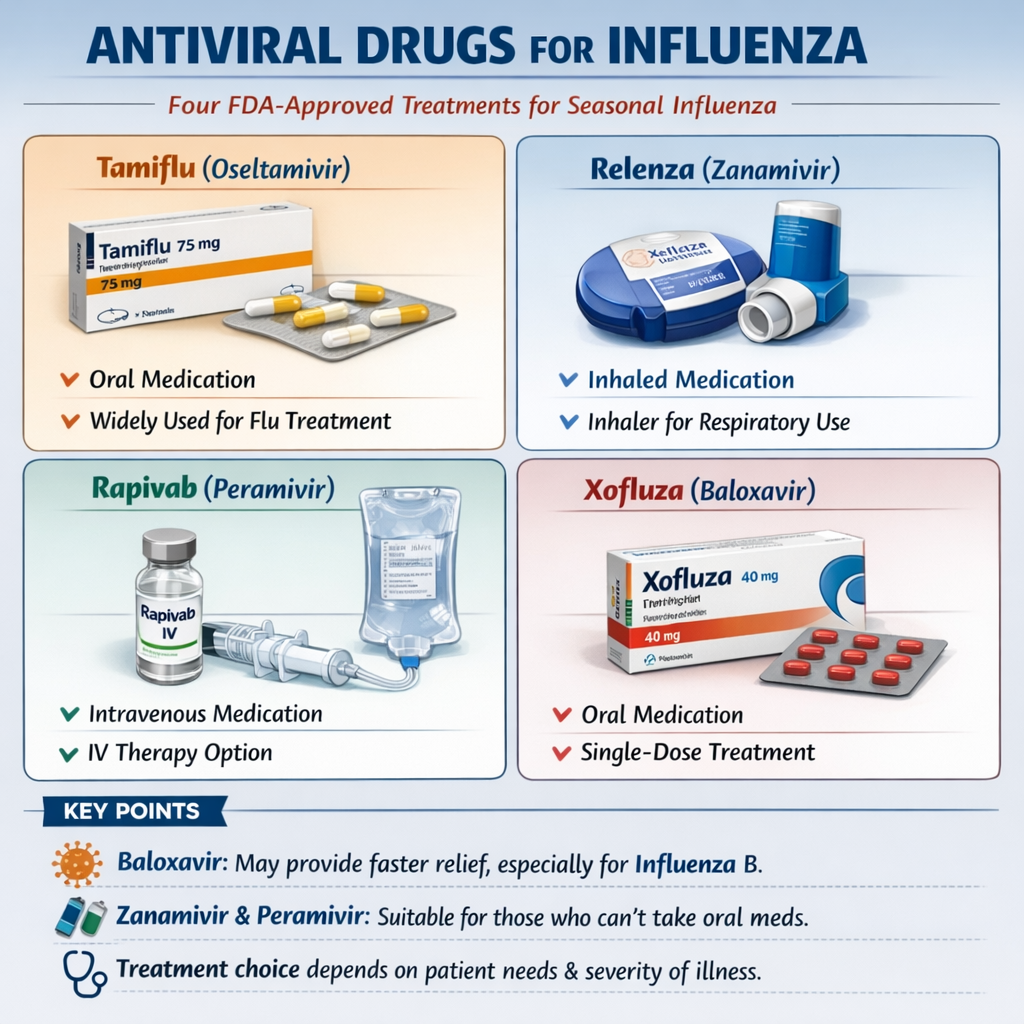
Beyond Tamiflu: Complete Guide to Flu Treatment Alternatives and Antiviral Options
While Tamiflu (oseltamivir) has dominated conversations about flu treatment for decades, it is far from the only antiviral medication available for combating influenza. The FDA currently recommends four antiviral drugs for treating seasonal influenza: oral oseltamivir (Tamiflu), inhaled zanamivir (Relenza), intravenous peramivir (Rapivab), and oral baloxavir marboxil (Xofluza). Each medication operates through different mechanisms, offers distinct advantages, and may be more suitable for specific patient populations. Recent clinical evidence demonstrates that baloxavir may provide faster symptom relief in some cases, particularly for influenza B infections, while zanamivir and peramivir offer alternatives for patients who cannot tolerate or absorb oral medications. Understanding these options empowers patients and healthcare providers to select treatments optimized for individual circumstances, severity of illness, and patient-specific factors that influence medication efficacy and tolerability.
 Health
Health
Gene Therapy for Inherited Retinal Diseases: From Bench to Bedside—Evolving Clinical Realities
Gene therapy has emerged from decades of theoretical research into clinical reality, marking a transformative milestone for treating inherited retinal diseases (IRDs). The 2017 FDA approval of voretigene neparvovec-rzyl (Luxturna), the first gene therapy for an inherited retinal disease targeting biallelic RPE65 mutations, demonstrated that gene replacement strategies could restore functional vision in patients with previously untreatable conditions. Clinical experience from early-adopter centers, including the University Eye Hospital of Ludwig Maximilian University Munich, reveals that while voretigene neparvovec delivers meaningful functional benefits—particularly improved light sensitivity and navigational vision—it does not halt retinal degeneration and works best with early intervention. The field is rapidly expanding beyond RPE65 disease, with emerging therapies in clinical trials targeting ABCA4-associated Stargardt disease, RPGR-mediated X-linked retinitis pigmentosa, and other IRDs. Success requires not only scientific innovation but also operational infrastructure, multidisciplinary patient selection processes, and realistic patient education about outcomes and expectations.
 Health
Health
Tramadol for Chronic Pain: Why This Popular Opioid May Do More Harm Than Good
A comprehensive systematic review of 19 randomized clinical trials involving 6,506 participants, published in BMJ Evidence-Based Medicine in December 2025, reveals that tramadol—a widely prescribed "safer" opioid for chronic pain—provides only minimal pain relief while substantially increasing the risk of serious adverse effects. The analysis found that tramadol reduces pain by less than clinically meaningful levels and doubles the risk of cardiac events, including chest pain, coronary artery disease, and congestive heart failure. With the global opioid crisis claiming approximately 600,000 lives annually and opioid-related overdose deaths in the United States increasing from 49,860 in 2019 to 81,806 in 2022, researchers conclude that tramadol's modest benefits are significantly outweighed by its potential harms, and its use should be minimized wherever possible in favor of safer, evidence-based alternatives.
 Health
Health
Safer Weight Loss Drugs: How Mitochondrial Uncoupling Helps Cells Burn More Calories Naturally
Revolutionary research from the University of Technology Sydney and Memorial University of Newfoundland has unveiled a safer approach to weight loss medications through controlled mitochondrial uncoupling. Scientists have developed experimental arylamide compounds that enhance cellular energy expenditure without the dangerous side effects of historical uncoupling drugs. By carefully tuning the chemical structure of these molecules, researchers can now achieve mild mitochondrial uncoupling that increases calorie burning while preserving essential ATP production and reducing oxidative stress. This breakthrough offers a promising new pathway for treating obesity and metabolic diseases while maintaining overall health and safety.
 Health
Health
Ultra-Processed Foods in India: How Rising Consumption Fuels the NCD Crisis and Threatens Public Health
Ultra-processed foods (UPFs) have become a significant public health threat in India, driving a rapid surge in non-communicable diseases (NCDs) including obesity, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular disease. With UPF retail sales skyrocketing from $0.9 billion in 2006 to nearly $38 billion in 2019—representing a staggering 40-fold increase—India now witnesses the fastest UPF sales growth worldwide. This comprehensive guide explores how ultra-processed foods fuel India's NCD burden, examines the mechanisms of harm, identifies key risk factors, and outlines evidence-based policy interventions needed to combat this escalating health crisis.
 Health
Health
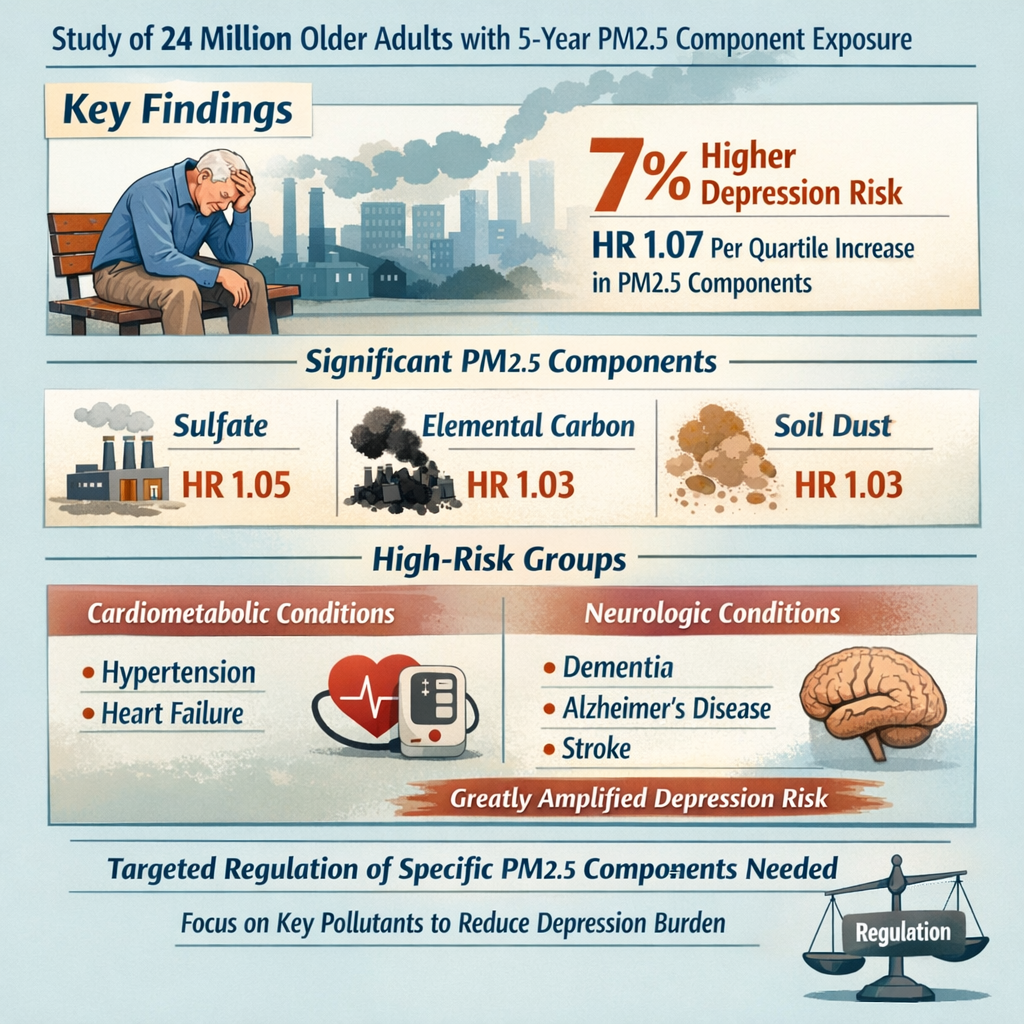
Three PM2.5 Components Drive Depression Risk in Older Adults: Sulfate, Elemental Carbon, and Soil Dust Analysis
A large cohort study of 24 million older adults demonstrates that specific PM2.5 components are significantly associated with increased depression risk, with sulfate, elemental carbon, and soil dust as primary contributors. The study used spatiotemporal modeling to assess 5-year average exposure to six PM2.5 components, finding that combined exposure increased depression risk by 7% (HR 1.07) with each quartile increase. Individual components showed depression associations: sulfate (HR 1.05), elemental carbon (HR 1.03), and soil dust (HR 1.03). Notably, vulnerable populations with cardiometabolic comorbidities (hypertension, congestive heart failure) or neurologic conditions (dementia, Alzheimer's disease, stroke) showed dramatically amplified depression risk. The findings suggest targeted regulation of specific PM2.5 components rather than total mass reduction may more effectively reduce depression burden, particularly among high-risk older adults.
 Health
Health
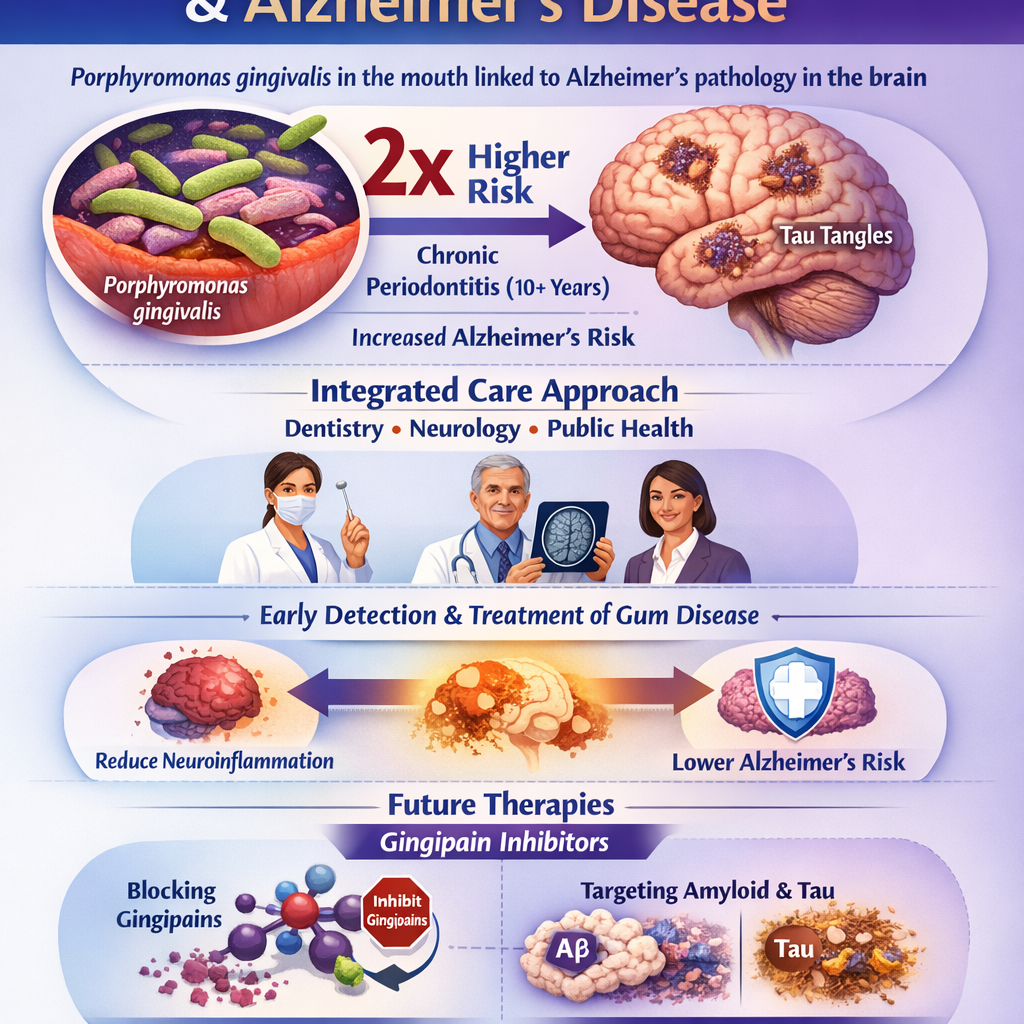
Oral Bacteria and Alzheimer's Disease Connection: How Periodontal Pathogen Porphyromonas Gingivalis Contributes to Neurodegeneration
Emerging research indicates a significant biological connection between periodontal disease and Alzheimer's disease, with Porphyromonas gingivalis—the keystone pathogen of periodontitis—identified in Alzheimer's disease brains where its toxic proteases called gingipains drive hallmark pathology including amyloid-beta accumulation and tau hyperphosphorylation. Epidemiological studies demonstrate that chronic periodontitis (10+ years) approximately doubles Alzheimer's disease risk, positioning oral health as a modifiable dementia risk factor. An integrated care model uniting dentistry, neurology, and public health is recommended, emphasizing earlier recognition and treatment of periodontitis as an underutilized strategy to reduce neuroinflammatory burden and potentially mitigate Alzheimer's disease risk. Future therapeutic approaches including gingipain inhibitors show promise in experimental models for reversing Alzheimer's-like pathology, suggesting targets for disease modification once clinically available.
 Health
Health
Dietary Vitamin C Physically Changes Your Skin: University of Otago Research Reveals Collagen Production and Skin Renewal Benefits
New research from the University of Otago, published in the Journal of Investigative Dermatology, demonstrates that dietary vitamin C dramatically improves skin health through collagen production and cellular renewal. The study found that vitamin C from food travels through the bloodstream into all skin layers, with skin cells demonstrating exceptional efficiency at extracting vitamin C from blood. Participants consuming two SunGold kiwifruit daily (250mg vitamin C) for eight weeks showed measurable increases in skin thickness, collagen production, and epidermal cell renewal rates. The research reveals that dietary vitamin C is approximately 20 times more effective than topical applications due to superior penetration and sustained delivery. The tight correlation between blood and skin vitamin C levels (stronger than any other organ studied) indicates skin prioritizes vitamin C uptake, supporting recommendations of 250mg daily through vitamin C-rich fruits and vegetables.
 Health
Health
Nebokitug Monoclonal Antibody: Game-Changing Treatment for Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis Shows Safety and Reduces Liver Fibrosis in Clinical Trial
A groundbreaking Phase 2 clinical trial led by University of California-Davis demonstrates that nebokitug, a novel monoclonal antibody, offers fresh hope for patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC)—a rare liver disease affecting 1 in 10,000 people with limited treatment options beyond transplantation. The trial published in the American Journal of Gastroenterology proves nebokitug is safe and effectively reduces liver inflammation, fibrosis markers (PRO-C3), and liver stiffness in PSC patients who previously faced inevitable disease progression and organ transplantation, positioning this targeted immunotherapy as a potential life-changing treatment.
 Health
Health
Scientists Reverse Alzheimer's Disease in Mice and Restore Memory: Breakthrough Study Shows Disease May Be Reversible Through NAD+ Balance Restoration
A groundbreaking study published in Cell Reports Medicine demonstrates that scientists have reversed Alzheimer's disease in mouse models and fully restored memory by restoring NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) balance in the brain. Researchers found that severe NAD+ depletion drives Alzheimer's pathology, and treating advanced-stage mice with P7C3-A20 compound repaired brain damage, reversed cognitive decline, and normalized tau-217 biomarkers—challenging the long-held assumption that Alzheimer's is irreversible and opening doors for future human clinical trials.
 Health
Health
How to Prep Your Mind, Body, and Nervous System for 2026: Complete Wellness Guide for Nervous System Regulation and Holistic Health
Prepare for 2026 with a comprehensive guide to nervous system optimization, mind-body wellness, and holistic health preparation. Learn science-backed strategies for nervous system regulation through movement, sleep optimization, mindfulness practices, vagus nerve activation, and integrative wellness approaches. Expert guidance covers parasympathetic nervous system activation, stress resilience, emotional regulation, and practical techniques to achieve personal coherence and lasting well-being heading into the new year.
 Health
Health
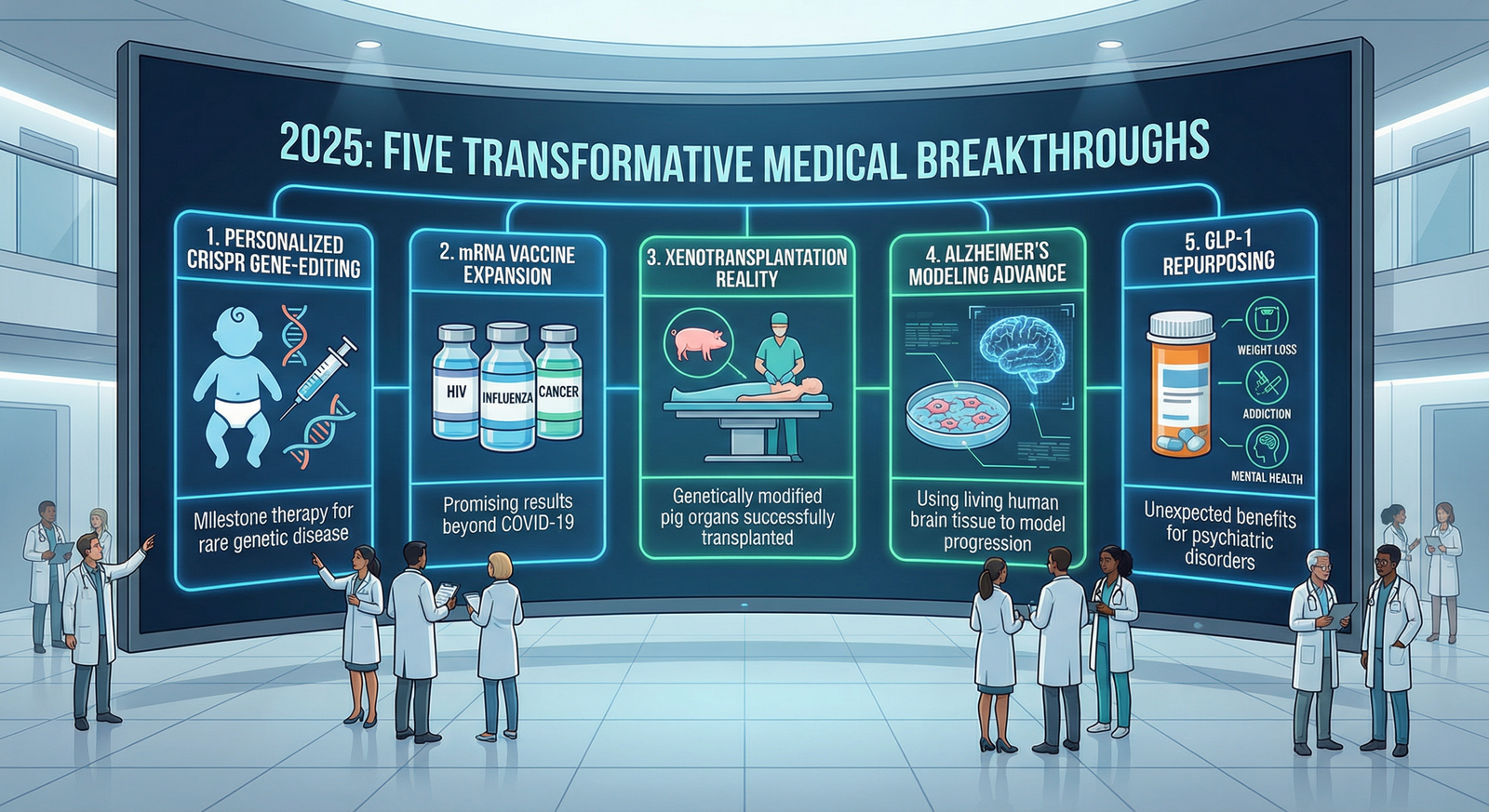
5 Medical Breakthroughs of 2025 That Give Hope: CRISPR Gene Therapy, mRNA Vaccines, Xenotransplantation, and Dementia Research
2025 witnessed five transformative medical breakthroughs that fundamentally advance healthcare innovation. A baby received personalized CRISPR gene-editing therapy for a rare genetic disease, marking a milestone in gene therapy. mRNA vaccine technology expanded beyond COVID-19 to HIV, influenza, and cancer applications with promising early results. Genetically modified pig organs were successfully transplanted into living human patients, moving xenotransplantation toward clinical reality. Scientists used living human brain tissue to model Alzheimer's dementia progression. GLP-1 weight loss drugs showed unexpected benefits for addiction and psychiatric disorders—together representing revolutionary advances transforming future healthcare delivery globally.
 Health
Health
Why Stroke Risk Increases in Winter: Neurosurgeon Explains How Cold Weather Affects Brain Blood Flow and Cerebral Circulation
Neurosurgeons warn that stroke risk significantly increases during colder months due to physiological changes in the human body triggered by low temperatures. Cold weather causes blood vessel constriction, blood thickening, increased blood pressure, morning temperature spikes, and elevated infection rates—all combining to heighten stroke vulnerability. Understanding these winter stroke mechanisms and implementing preventive strategies like staying active, managing chronic conditions, and recognizing FAST stroke warning signs can protect health during winter months.
 Health
Health
Synbiotics Improve Diabetes Risk Factors in Elderly Patients: Clinical Trial Shows Weight Loss and Metabolic Benefits
A randomized controlled trial involving 96 elderly patients with type 2 diabetes demonstrates that multi-species synbiotic supplementation significantly improves key cardiovascular and metabolic risk factors. Over four months, synbiotic treatment produced clinically meaningful weight loss (1.16 kg), reduced fasting glucose (22.83 mg/dL), improved insulin resistance, decreased LDL cholesterol (10.83 mg/dL), and lowered vascular inflammation markers—offering a safe, adjunctive approach to managing diabetes and cardiovascular risk in aging populations.
 Health
Health
Top 10 Oncology On the Go Podcast Episodes of 2025: Essential Clinical Insights and Practice-Changing Updates from Experts
CancerNetwork's "Oncology On the Go" podcast delivered 10 standout episodes in 2025 covering breakthrough treatments, clinical conference data, and psychosocial oncology insights. Episodes featured expert discussions on tarlatamab for small cell lung cancer, lung cancer advances from ASCO Annual Meeting, COVID-19's lasting impact on cancer care, amivantamab management, CAR-T cellular therapy innovations, low-grade serous ovarian cancer treatment paradigms, and mental health considerations in oncology—providing clinicians with essential, evidence-based content for improved patient outcomes.
 Health
Health
WHO Updated HIV Clinical Management Recommendations 2025: Revolutionary Guidelines for Antiretroviral Therapy and Vertical Transmission Prevention
The World Health Organization released updated clinical management recommendations for HIV emphasizing optimized antiretroviral therapy (ART) regimens, advanced prevention of vertical transmission, and enhanced tuberculosis preventive treatments. These evidence-based guidelines target the global initiative to end AIDS as a public health threat by 2030, providing simplified treatment protocols, innovative drug formulations, and breastfeeding guidance that balance transmission prevention with maternal-infant health outcomes across diverse global healthcare settings.
 Health
Health
Bird Flu 2026: Scientists Warn H5N1 Could Spark Human Pandemic as Global Outbreak Spirals Out of Control
Leading virologists warn that H5N1 bird flu has reached alarming levels as 2026 begins, with 180+ million poultry infected in the US alone and the virus spreading across unprecedented mammalian species including dairy cattle. With only a 2-10 case window for pandemic containment and growing human infections, experts emphasize urgent need for coordinated global surveillance, vaccination programs, and transparency to prevent catastrophic human-to-human transmission.
 Health
Health
Pan-European Study Reveals High Prevalence of Addictive Behaviors in Chronic Skin Disease Patients
A comprehensive pan-European study across 20 countries involving 3,585 patients with chronic skin diseases reveals alarming prevalence rates of addictive behaviors including smoking (25.7%), internet addiction (29.7%), hazardous drinking (8.8%), and drug use disorders (5.3%). The research highlights significant associations between chronic skin conditions, psychological distress, and maladaptive coping mechanisms, emphasizing the critical need for multidisciplinary care and routine addiction screening in dermatological settings.
 Health
Health
Ben Sasse Cancer Diagnosis: Former Senator Announces Stage 4 Pancreatic Cancer with "Death Sentence" Prognosis
On December 23, 2025, former Republican Senator Ben Sasse stunned everyone with some heartbreaking news. At 53, he announced he has stage 4 pancreatic cancer, and it’s already spread. He opened up about it in a long post on X (that’s what Twitter’s called now), calling advanced pancreatic cancer “a death sentence.” He didn’t sugarcoat it—he just said, “am gonna die.” Even with that blunt honesty, Sasse talked about fighting hard and making the most of his time with his family. His announcement hit a nerve, not just in politics but everywhere. Support poured in from old colleagues, friends, and a lot of people who just wanted to let him know they care.
 Health
Health
SA-XV Peptide Therapy: Revolutionary Treatment for Fungal Keratitis and Eye Infections
Fungal keratitis is a tough, often dangerous infection of the cornea, and honestly, doctors haven’t had many good ways to treat it. But now, researchers from the L V Prasad Eye Institute in Hyderabad and the Bose Institute in Kolkata have come up with something new: SA-XV peptide therapy. This antimicrobial peptide, based on the host-defense peptide S100A12, looks really promising. It tackles fungal eye infections head-on and does it without the nasty side effects you usually get from standard antifungal drugs.
 Health
Health
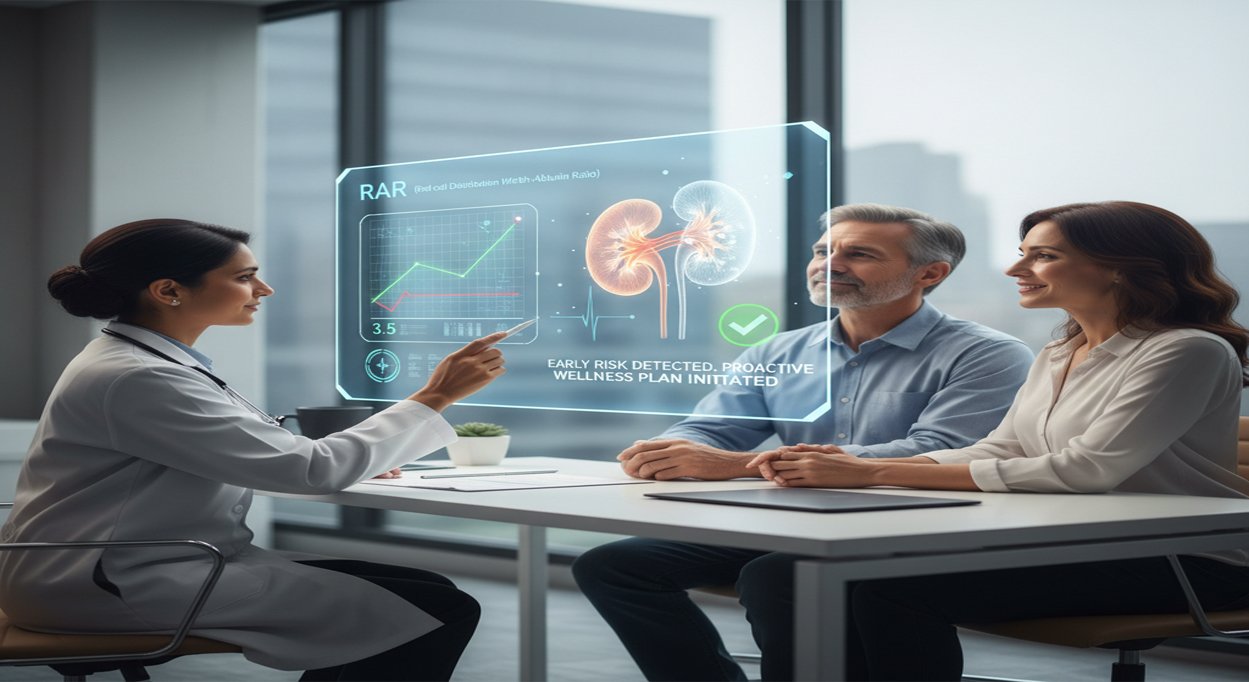
Red Cell Distribution Width-to-Albumin Ratio (RAR): Novel Inflammatory Marker for Diabetic Kidney Disease Risk Prediction
Looking at how inflammation ties into kidney health in people with diabetes is a big deal, honestly. Diabetic kidney disease (or DKD, if you want to sound like you’re in the know) is one of the toughest problems for anyone living with diabetes. It affects millions, and it’s a huge burden. But here’s what’s exciting—recent research has turned up something pretty important. Scientists dug into a huge set of US health data and found that a simple lab measure, the red cell distribution width-to-albumin ratio (RAR), links closely to who ends up developing DKD. Basically, RAR puts together two things doctors already check—how varied your red blood cells are, and your albumin levels. Turns out, this combo can really tell you who’s at higher risk. This kind of insight could totally change how doctors spot risk early and jump in with care before things get worse. It’s a big step toward better outcomes for people living with diabetes.
 Health
Health
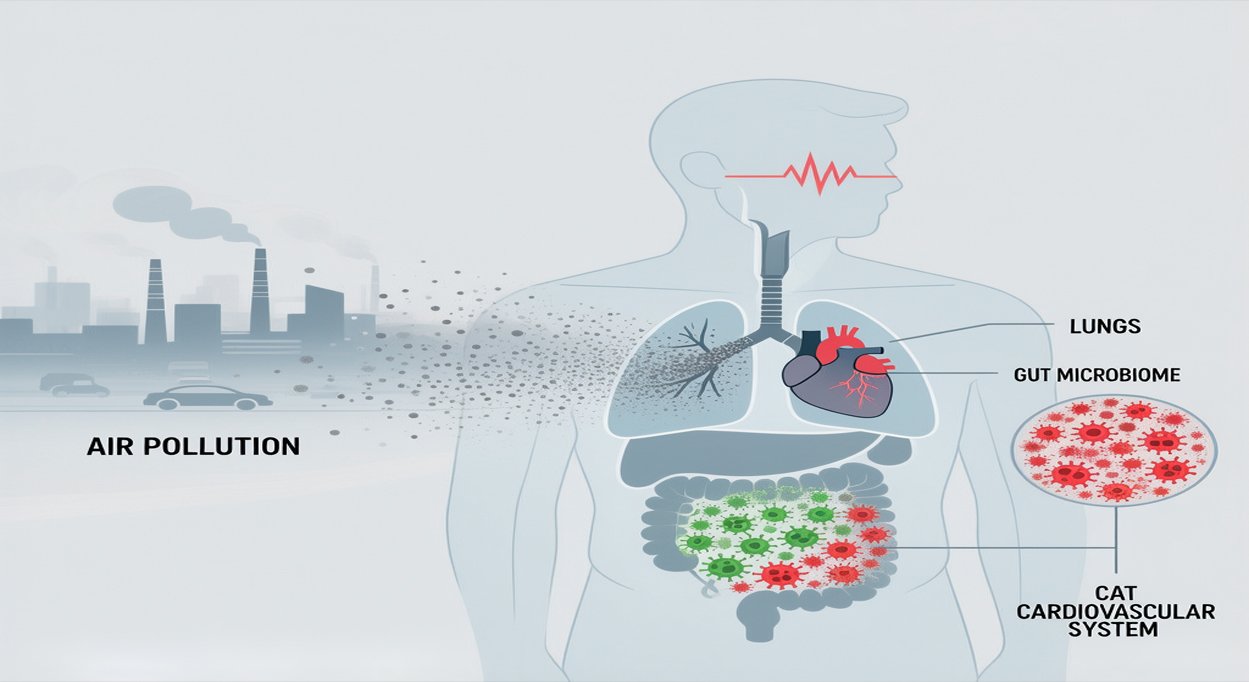
Pollution Alters Gut Health and Harms Your Heart: A Comprehensive Medical Guide
New research is shining a light on just how much air pollution messes with our bodies—not just our lungs. Turns out, breathing in all that fine particulate matter actually changes the bacteria living in your gut, weakens your intestinal barrier, and raises your risk for some nasty heart problems like heart attacks and strokes. It’s a bigger deal than most people realize. Air pollution isn’t just an environmental issue; it’s a real public health threat, touching billions of lives. Knowing how it works helps people take steps to protect themselves.
 Health
Health
How Skipping Breakfast Can Spike Your Cholesterol: A Complete Guide to Heart-Healthy Morning Habits
Skipping breakfast might feel like a quick fix when mornings get hectic, but it can quietly push your cholesterol higher over time. Around 15% of American adults skip breakfast every day, and most have no idea this habit messes with their heart health. When you pass on that first meal, you throw off your body’s natural rhythm—the one that helps keep your cholesterol in check. Without those early nutrients, your liver kicks into overdrive and cranks out more cholesterol, especially the LDL kind you definitely don’t want. The fix? Just eat a balanced breakfast. It doesn’t have to be complicated, but it can make a real difference in keeping your cholesterol—and your heart—in good shape.
 Health
Health
6 Best Magnesium-Rich Foods to Prevent Fatty Liver: Expert-Approved Guide to Liver Health
Top 6 Magnesium-Rich Foods to Help Prevent Fatty Liver Fatty liver isn’t just something heavy drinkers have to worry about anymore. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) now affects millions of people, no matter their age or how healthy they think they are. The good news? What you eat makes a big difference. Lately, researchers have zeroed in on magnesium, and the results are pretty clear—people who get more magnesium in their diets tend to have healthier livers. It’s not just a small difference, either. There’s a real link between higher magnesium intake and lower rates of fatty liver disease. So, if you want to protect your liver, paying attention to magnesium is a smart move. Let’s get into it. Here are six of the best magnesium-rich foods you can start adding to your meals right now. They’re simple, they taste good, and they give your liver the support it needs to stay healthy.
 Health
Health
Big Questions Swirl Around CDC’s Controversial Hepatitis B Vaccine Policy Shift
For over thirty years, the U.S. has followed a simple rule: every newborn gets the hepatitis B vaccine within 24 hours of birth. Now, in a move that’s left a lot of doctors frustrated, the CDC’s vaccine advisory panel just voted to toss that rule out for most babies. Instead, parents of infants born to mothers who test negative for hepatitis B can wait until their child turns two months old before getting the shot—or skip it altogether. The vote wasn’t even close: 8 to 3. That’s a huge change, and it’s already touched off a wave of debate about the science behind it and what this might mean for how vaccines are handled in the future, especially under the Trump administration.